
- #GIT CREATE BRANCH CHECKOUT HOW TO#
- #GIT CREATE BRANCH CHECKOUT INSTALL#
- #GIT CREATE BRANCH CHECKOUT CODE#
VS Code's Git services will still work as usual, showing all changes within the repository, but file changes outside of the scoped directory are shaded with a tool tip indicating they are located outside the current workspace.
#GIT CREATE BRANCH CHECKOUT CODE#
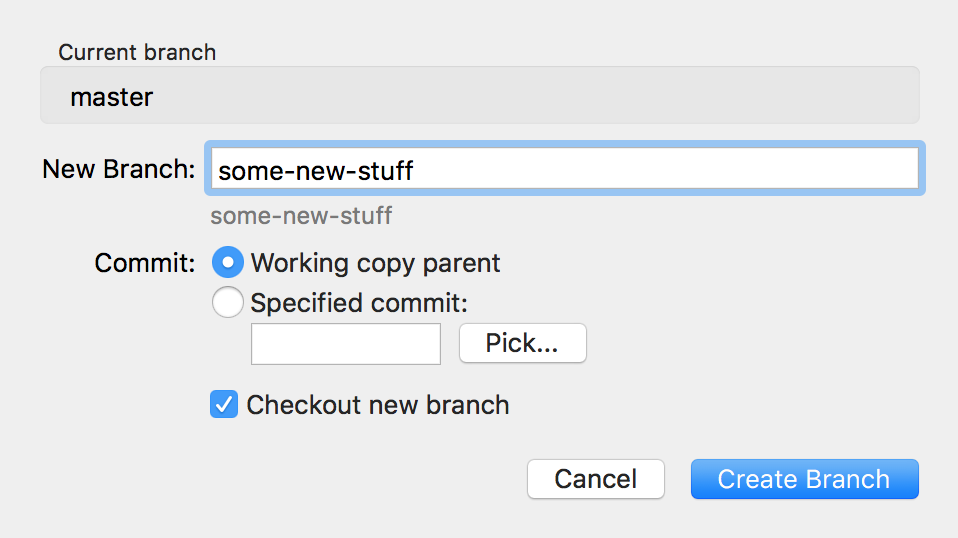
Tip: You can open VS Code in a sub-directory of a Git repository. You can checkout any branch in your repository by clicking that status indicator and selecting the Git reference from the list. You can also find indicators of the status of your repository in the bottom-left corner of VS Code: the current branch, dirty indicators, and the number of incoming and outgoing commits of the current branch. Note that for unstaged changes, the editor on the right still lets you edit the file: feel free to use it! Selecting the icon will show you the details of your current repository changes: CHANGES, STAGED CHANGES and MERGE CHANGES.Ĭlicking each item will show you in detail the textual changes within each file. The Source Control icon in the Activity Bar on the left will always indicate an overview of how many changes you currently have in your repository. You can find the details in Git commit information. 👉 When you commit, be aware that if your username and/or email is not set in your Git configuration, Git will fall back to using information from your local machine.
#GIT CREATE BRANCH CHECKOUT INSTALL#
Make sure you install at least version 2.0.0. Note: VS Code will leverage your machine's Git installation, so you need to install Git first before you get these features. The VS Code documentation assumes you are already familiar with Git. Note: If you are new to Git, the git-scm website is a good place to start, with a popular online book, Getting Started videos and cheat sheets.
#GIT CREATE BRANCH CHECKOUT HOW TO#
Most of the source control UI and work flows are common across other SCM extensions, so reading about the general Git support in VS Code will help you understand how to use another provider. VS Code ships with a Git source control manager (SCM) extension. Select providers" to see available SCM providers.

Start typing and you will see suggestions for extension categories like debuggers and linters. If you would like to install another SCM provider, you can search on the scm providers extension category in the Extensions view ( ⇧⌘X (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+X)). The Source Control Providers view shows the detected providers and repositories, and you can scope the display of your changes by selecting a specific provider. To turn on the Source Control Providers view, select the overflow menu in the Source Control view ( ⌃⇧G (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+G)), hover over Views, and make sure that Source Control Repositories is marked with a check. For example, you can open multiple Git repositories alongside your Azure DevOps Server local workspace and seamlessly work across your projects. VS Code has support for handling multiple Source Control providers simultaneously. Tip: Click on an extension tile to read the description and reviews in the Marketplace.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
